Preventive Care and Education for Lasting Periodontal Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the health of your gums, teeth, and overall smile. This condition progresses gradually, often starting with subtle symptoms that may go unnoticed. Recognizing the signs early and understanding the risk factors can play a significant role in prevention and treatment.
If you notice any symptoms discussed below, we encourage you to reach out to our Loveland, OH office for a consultation. Dr. Michael Kreimer and our experienced dental team are here to provide you with comprehensive care, helping you manage and treat any stage of gum disease. Call us today at (513) 677-3656 to schedule an appointment.
Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
Healthy gums should feel firm and look pale pink. However, if your gums appear red, swollen, or are tender to the touch, this could be an early indication of gum disease. Redness in the gums occurs as the body’s natural response to infection, increasing blood flow to the affected area. Swelling and tenderness often accompany this redness, making the gums sensitive to brushing and flossing.
Bleeding Gums
One of the most recognizable symptoms of gum disease is bleeding during brushing or flossing. This symptom is common in the early stages of gingivitis and can become more pronounced as the disease progresses. Noticing blood on your toothbrush or in the sink should be a warning sign to seek professional dental attention. Untreated gum inflammation can worsen, causing the gums to bleed more frequently and leading to further complications.
Receding Gums
As periodontal disease advances, you may observe that your gums are pulling away from the teeth. This gum recession exposes the roots of your teeth, which are more sensitive and prone to decay. Receding gums can also create pockets where bacteria accumulate, further exacerbating gum disease. With exposed roots, you may experience heightened sensitivity, making it uncomfortable to consume hot, cold, or sweet foods.
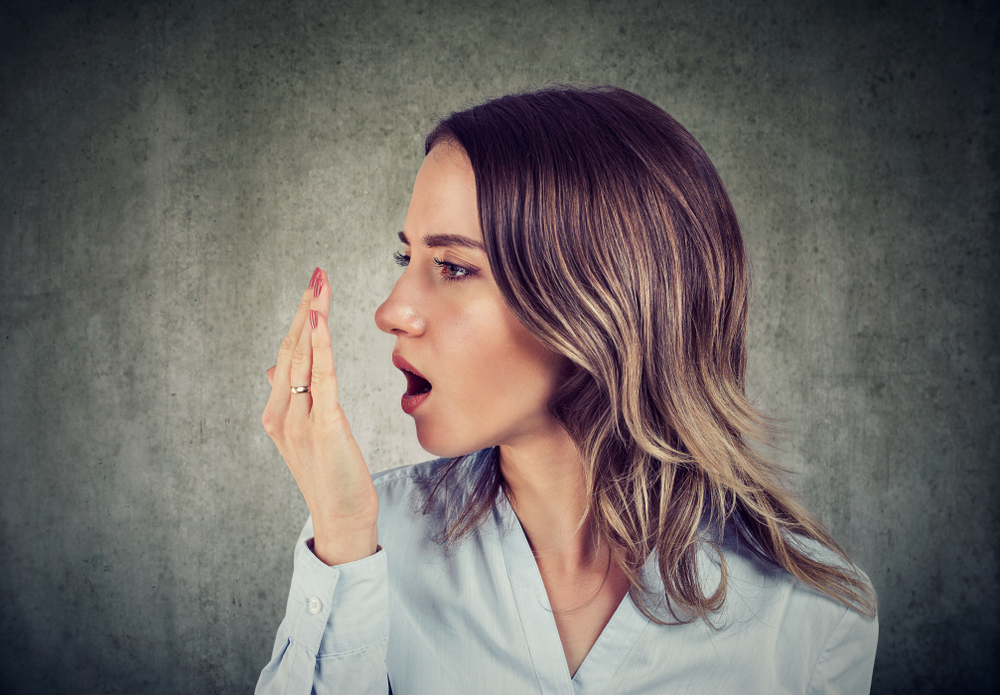
Bad Breath and Foul Taste
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, is often linked to gum disease. The bacterial buildup in plaque produces sulfur compounds that cause a foul smell. This odor can linger even after brushing, as the bacteria continue to thrive in the infected gum pockets. Additionally, you may experience a persistent bad taste in your mouth, which often indicates an underlying gum infection.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
In more advanced stages, gum disease can lead to the loosening or shifting of teeth. As the bone and gum tissue deteriorate, the teeth lose their stability. Loose teeth can disrupt your bite, affecting how you chew and speak. If left untreated, this stage of gum disease, called periodontitis, can ultimately result in tooth loss, severely impacting your oral health and smile.
Pus Between the Teeth and Gums
Pus is a clear indicator of infection and is often found between the teeth and gums in advanced gum disease. This buildup of pus, or gum abscess, may cause pain and a bad taste in the mouth. An abscessed area is usually sensitive to touch and may cause swelling in the surrounding gum tissue. Dental treatment is essential at this stage to prevent the spread of infection to surrounding tissues.

Primary Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Poor Oral Hygiene
Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque and tartar to build up on your teeth, leading to gum inflammation and infection. Without daily removal, this sticky film of bacteria can harden into tartar, which irritates the gums and promotes bacterial growth. Keeping up with daily oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease.
Tobacco Use
Smokers and those who chew tobacco are at a higher risk for developing gum disease. Tobacco weakens the immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight infection. Additionally, tobacco use reduces blood flow to the gums, delaying the healing process and making treatment for gum disease less effective.
Genetics
Your family history can play a role in your susceptibility to gum disease. Some people are genetically predisposed to periodontal disease, even if they maintain excellent oral hygiene. Understanding your genetic risks can help you and your dentist take proactive steps to monitor and protect your gum health.
Age
As we age, the risk of gum disease naturally increases. Older adults are more likely to experience issues like receding gums and bone loss, both of which contribute to periodontal disease. Regular dental visits become especially important with age to help catch signs of gum disease early and preserve oral health.
Diabetes
Diabetes can weaken the body’s ability to fight infection, making gum disease more likely. Diabetic patients may also experience dry mouth, which creates an ideal environment for bacteria. This combination of factors makes it essential for people with diabetes to maintain consistent dental care.
Medications
Certain medications, including antidepressants, heart medications, and some oral contraceptives, can increase the risk of gum disease. Many of these medications cause dry mouth, which reduces saliva production. Since saliva helps to wash away bacteria, a lack of it can lead to an increase in plaque buildup, increasing the risk of gum infection.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation, can increase gum sensitivity and susceptibility to disease. During these times, the gums may respond more intensely to plaque, leading to inflammation. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are important to help manage this increased risk.
Poor Nutrition
A diet high in sugars and carbohydrates feeds harmful bacteria in your mouth, encouraging gum disease. Nutrient deficiencies, especially in vitamin C, can weaken gum tissue and make it harder for your gums to recover from inflammation or infection. A balanced diet can support gum health and reduce the chances of developing periodontal disease.
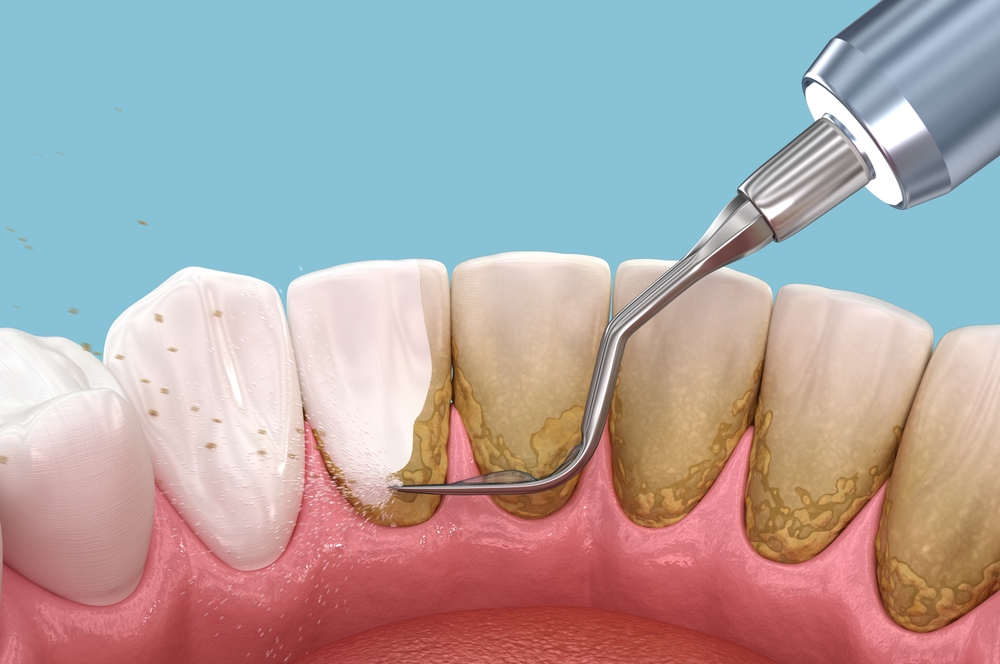
Our Gum Disease Treatment Options in Loveland, OH
Dr. Michael Kreimer offers advanced treatments for patients at our Loveland office to effectively manage gum disease. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of your condition. For early-stage gum disease, a professional cleaning may be sufficient to remove plaque and tartar. In more advanced cases, scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning procedure) can help remove bacteria and smooth the root surfaces, making it harder for plaque to accumulate.
For patients requiring additional care, Dr. Kreimer also offers periodontal maintenance to keep gums healthy and prevent the recurrence of gum disease. Our goal is to preserve your natural teeth and restore your gum health so you can smile confidently again.
Call our Loveland office today at (513) 677-3656 to learn more about our gum disease treatments and schedule a consultation. We are here to help you achieve a healthier smile with personalized, compassionate care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum disease be reversed?
Yes, in its early stages, gum disease can often be reversed with improved oral hygiene and professional dental cleanings. However, more advanced stages, such as periodontitis, may require specialized treatments to manage the condition.
How can I prevent gum disease?
To prevent gum disease, practice daily oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day and flossing once a day. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings, along with avoiding tobacco products and maintaining a healthy diet, are also effective preventive measures.
How do dentists treat gum disease?
Treatment varies based on severity but often begins with professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. For more advanced gum disease, treatments like scaling and root planing or surgical options may be recommended to restore gum health.
Is gum disease contagious?
Gum disease itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause it can be spread through saliva. Sharing utensils, toothbrushes, or other personal items can increase the risk of bacterial transfer, especially if one person already has gum disease.
Can gum disease lead to other health problems?
Yes, gum disease has been linked to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions. The inflammation associated with gum disease can impact other areas of the body, making it important to address the condition early.
Start Your Journey to Periodontal Wellness with Dr. Kreimer
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease, our Loveland team is here to provide compassionate care and effective treatment options. Dr. Michael Kreimer has the experience and expertise needed to address gum disease at any stage. We’ll help you regain your oral health and maintain a beautiful, confident smile. Contact us at (513) 677-3656 to book an appointment today.
Our Loveland practice also welcomes patients from surrounding areas, including Cincinnati, Hamilton, and Milford, OH. With a focus on high-quality dental care and personalized attention, we look forward to helping you improve your smile and oral health.


